There are two (or three) proper ways of updating Virtual Machine Scale Set instances:
- use custom images and update instances whenever something changes
- use VMSS Extension to install additional software on all the VM instances
- combine both
Possibly there’s a fourth way, but I haven’t investigated that yet. I am thinking of updating VMSS data disks on the fly, but I haven’t tried that yet. Let’s focus on using VMSS Extension. In this article I will show how to use new azure_rm_virtualmachinescalesetextension module. It’s already available in azure_preview_modules and will be released in Ansible 2.8.
Prerequisites
Before trying the playbooks, clone following repository:
1 2 | |
Step 1: Create VMSS using Ubuntu 16.04 Image
In this step we will just create Azure Virtual Machine Scaleset based using standard Ubuntu 16.04 image and all prerequisites.
Run following playbook:
1
| |
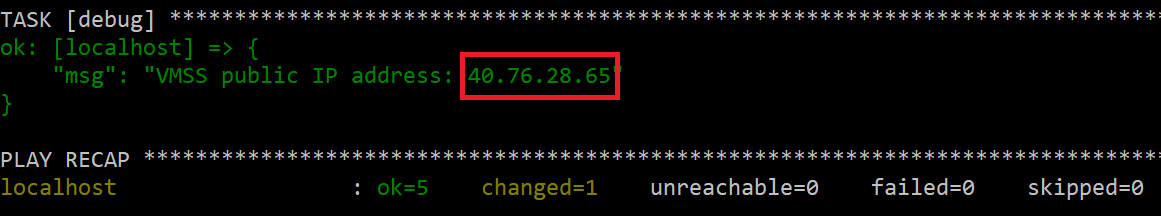
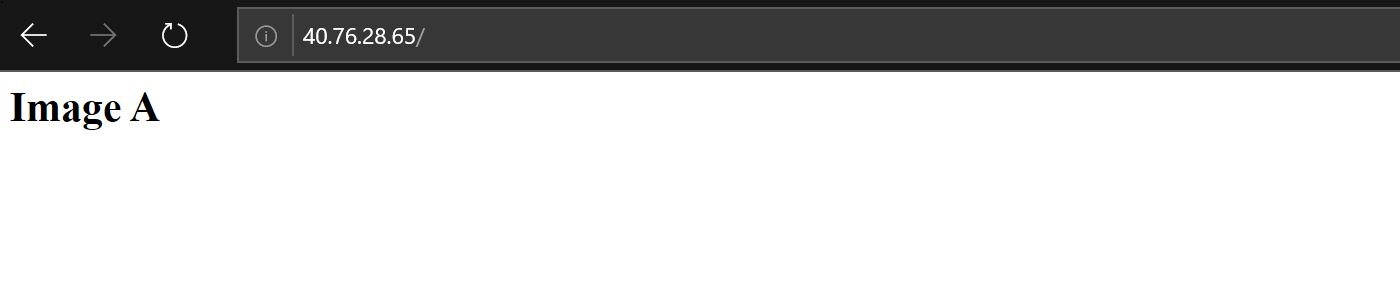
After this playbook is executed you will see an IP addres. Copy it to the browser. The page should fail to open as initial Ubuntu 16.04 image doesn’t have web server installed.
You can also go to Azure Portal and check the status of VMSS instances:
Step 2: Install VMSS extension
In second step we will install a Custom Script VMSS extension that will install httpd.
Run following playbook:
1
| |
In this step we use azure_rm_virtualmachinescalesetextension module:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | |
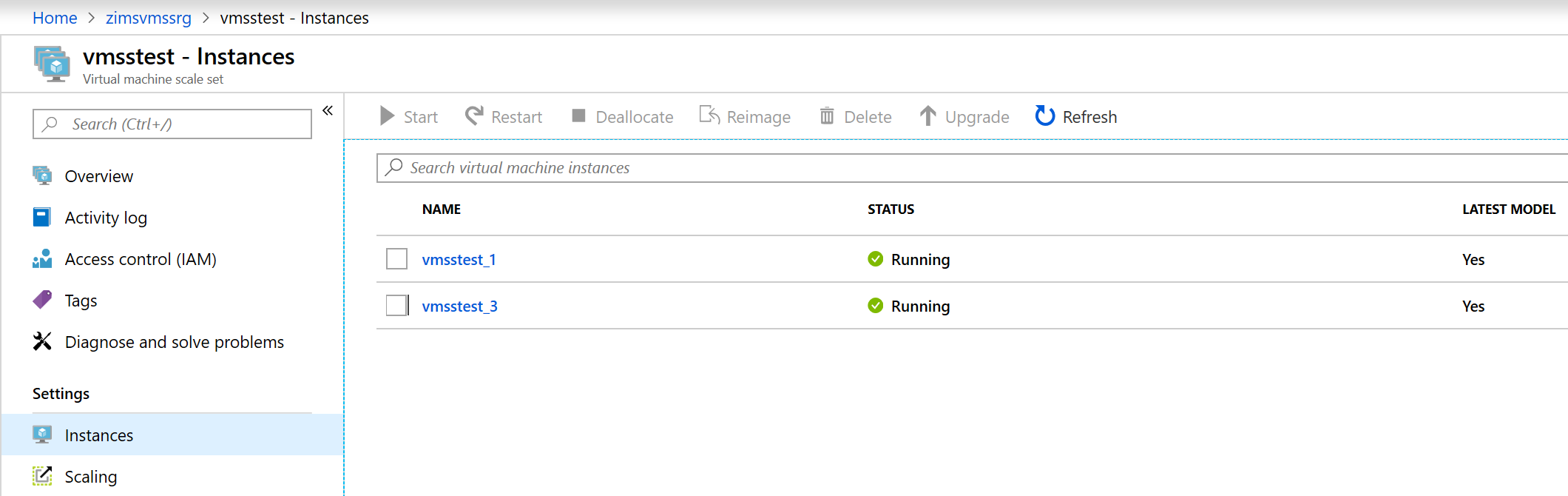
Please note that creating extension didn’t update existing instances. You can check how it looks in the portal again - as you see all the instances are not up to date:
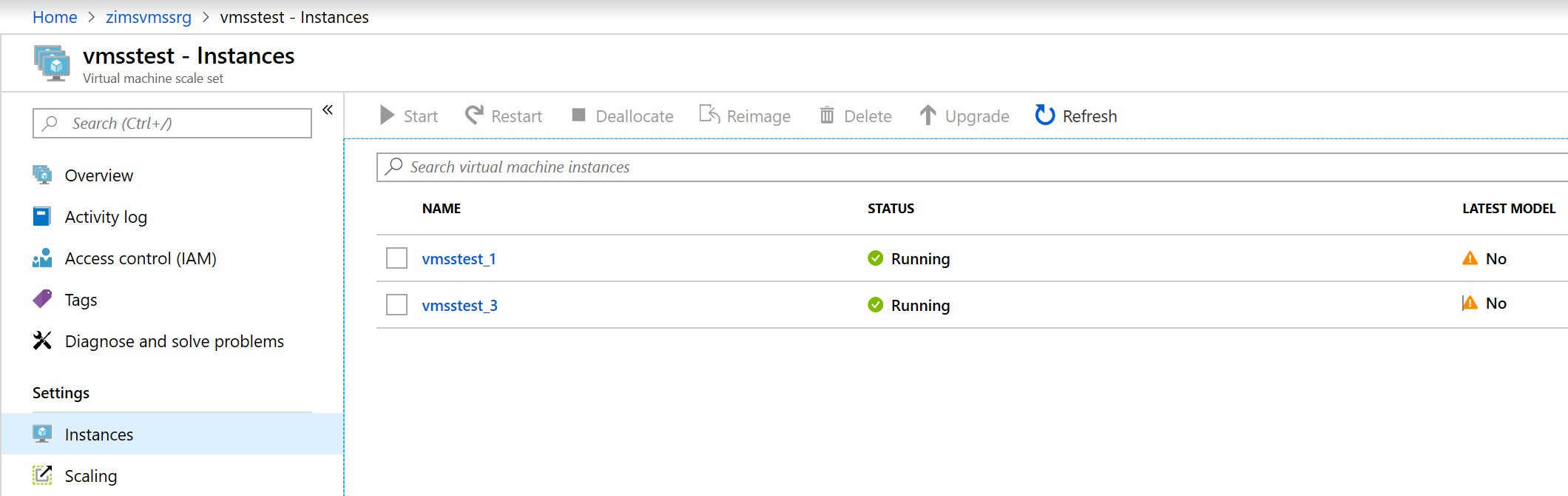
Step 3: Update all the instances
In this step we will actually upgrade all VM instances. Run following script:
1
| |
First azure_rm_virtualmachinescalesetinstance_facts module is used to get list of instances:
1 2 3 4 5 | |
And then azure_rm_virtualmachinescalesetinstance module to set latest_version to yes:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
Again, you can see in the portal how instances are being updated one by one:
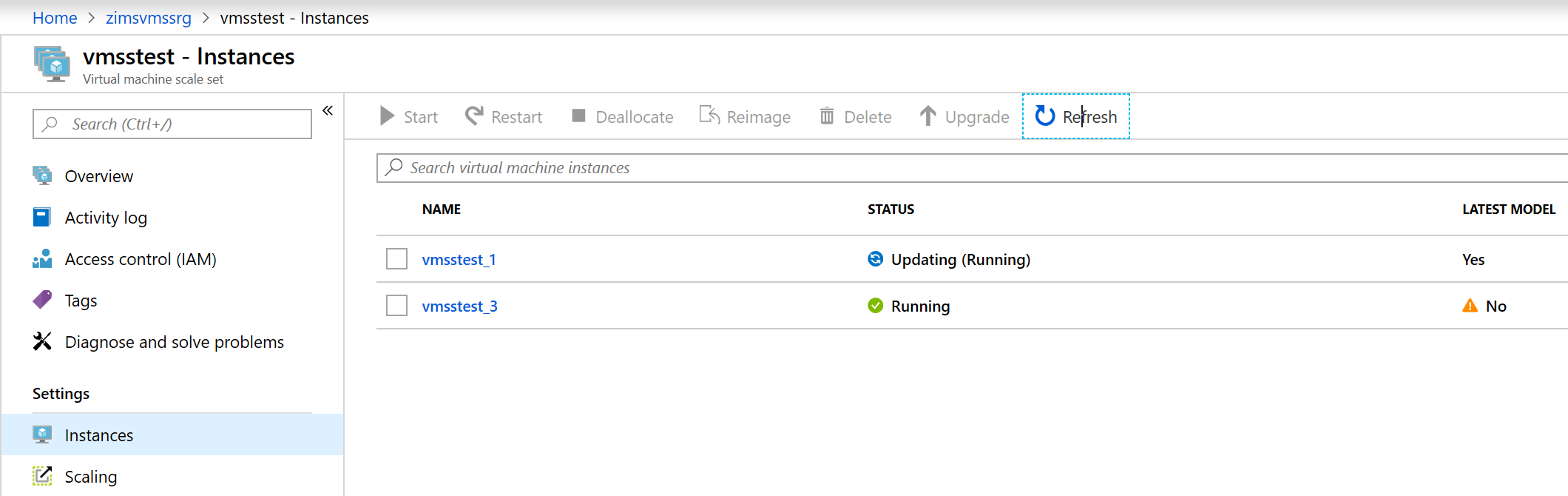
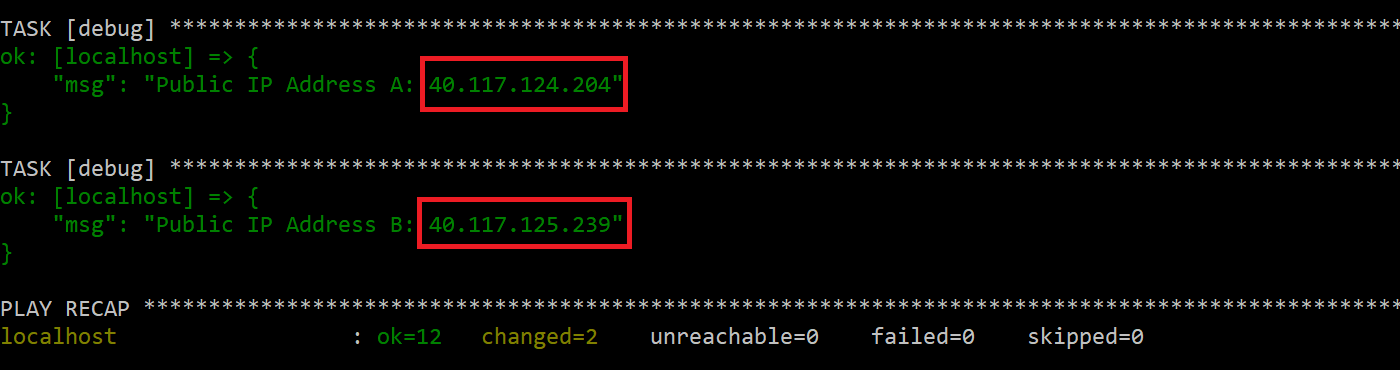
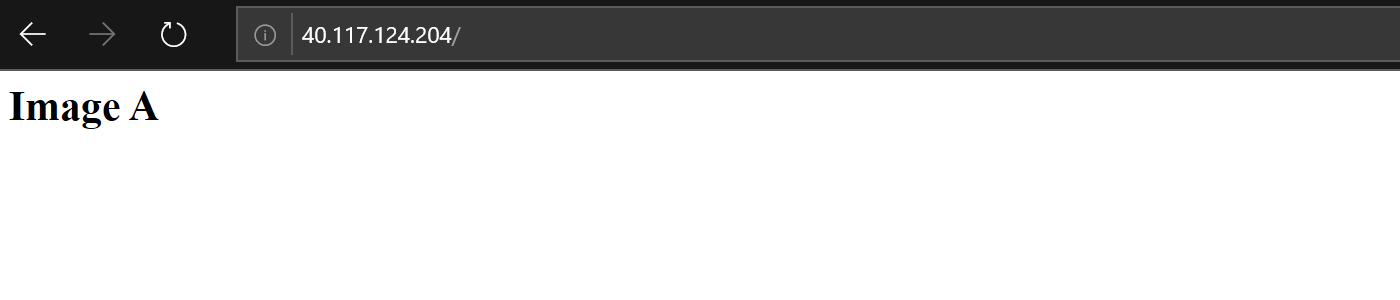
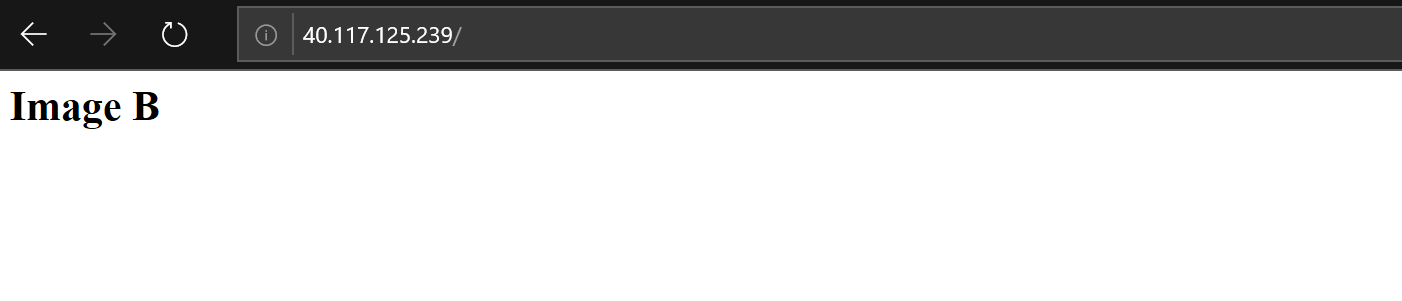
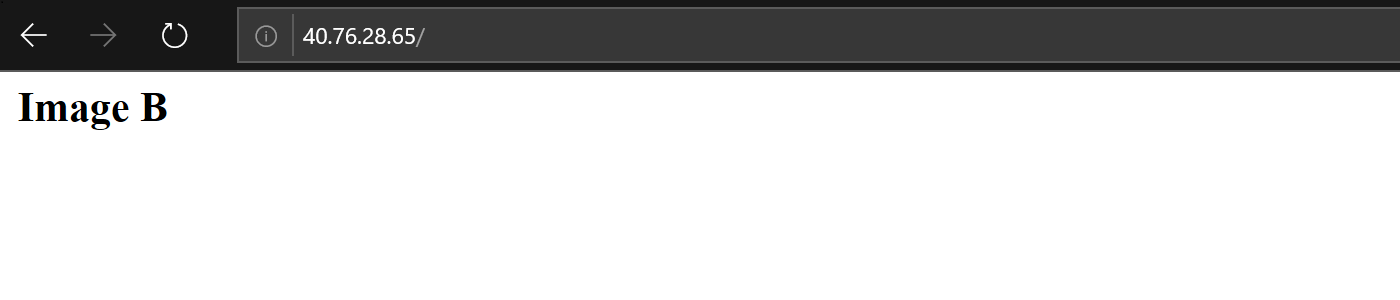
When update is completed reload the page, and you should see that this time default Apache index page is displayed: